
In the clinical setting, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a frequent, but under-diagnosed entity. This study shows that sulfate-reducing bacteria could convert available H2 to H2S, leading to measured hydrogen levels that are dependent on the actions of both H2 producers and H2 consumers. In the in vivo study, H2 concentrations were significantly higher in the B. theta groups (34.2 ± 29.8 ppm P < 0.05) H2S concentration was statistically higher in the combined group (10.32 ± 1.5 ppm) compared with B. In the in vitro experiment, H2 concentration was higher in the combined group (188 ± 93.3 ppm) compared with D. In the in vivo study Sprague–Dawley rats were gavaged with suspended bacteria in four groups: B. Gas samples were collected at 2 h and 24 h after incubation and assayed for H2, CH4, and H2S. theta, H2 producers), Desulfovibrio vulgaris (D.

In the in vitro study, groups were Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (B. We hypothesize that the availability of measured H2 depends on both hydrogen producers and hydrogen consumers by measuring H2 in vitro and in vivo. H2S is not measured in the evaluation of gaseous byproducts of microbial fermentation. Gut microbiome also includes H2-consuming microbes utilizing H2 for metabolism: methanogens producing methane, CH4, and sulfate-reducing bacteria producing hydrogen sulfide, H2S. Hydrogen gas (H2) is produced by H2-producing microbes in the gut during polysaccharide fermentation. SIBO therapy involves prescription of antibacterial agents, the most studied of which is the non-absorbable antibiotic rifaximin-α. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is common in patients with various diseases, but has non-specific manifestations, so proper diagnosis of this condition is required. The main approaches to the treatment of SIBO include the elimination of the underlying cause of its occurrence, the use of antibacterial drugs and adherence to dietary recommendations (elemental diet).Ĭonclusion. Specific methods for diagnosing SIBO are the culture method and breath tests. Most often, SIBO is associated with various chronic non- infectious diseases (both diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and the cardiovascular system and the neuromuscular apparatus) and can affect the severity of their symptoms.
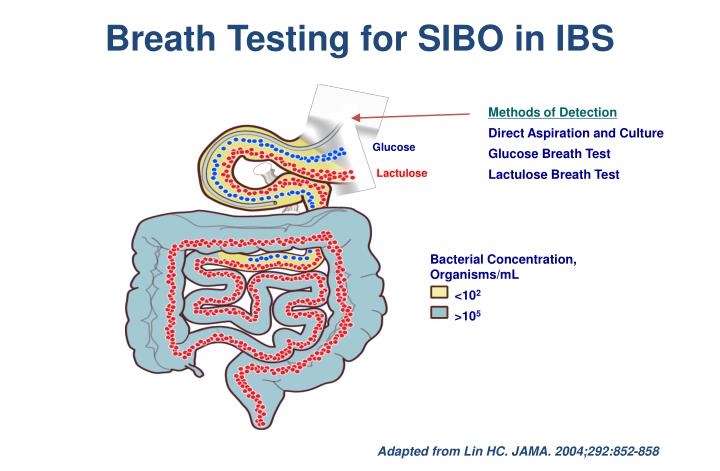
Clinically, the syndrome is manifested by nonspecific gastroenterological complaints and the development of malabsorption syndrome. SIBO is a condition characterized by an increased amount and/or abnormal composition of the microbiota in the small intestine.
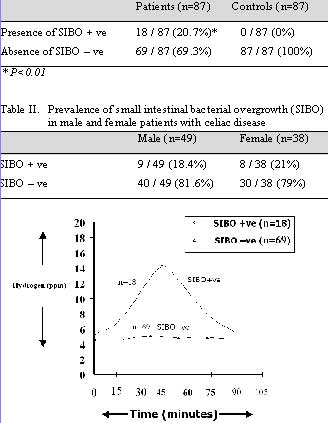
To optimize the choice of treatment strategies by physicians and gastroenterologists to improve treatment and prevention of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in adults.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
